In a tale that would have Edgar Allan Poe turning in his grave, a news article from Zimbabwe narrates the darker side of resurrection. In a July 26 story entitled “Schoolgirl ‘rises from the dead’” News Day online reports that a sixth form girl, after falling into a coma (the article says she had “fallen into a comma”-embarrassing enough under any circumstances) was pronounced dead and taken to the morgue. Her coughing, possibly from the cold, caught the attention of an attendant and she was rescued. Her schoolmates feared her until school authorities “assured them it (the mishap) was normal.” Even more disturbing is the sentence, “Cases of people gaining consciousness in the morgue after being certified dead are quite common and in most cases doctors would have erred.” The story serves a grim reminder of how in many parts of the world what is taken for granted in developed nations is still a desideratum.
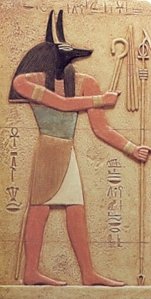
The fate of the dead is a major preoccupation of religion. Certainly among the most famous African outlooks on the subject, the Egyptians possessed a highly refined view of the life beyond. Having just covered Egyptian funerary beliefs in Ancient Near Eastern Religions class, the connection between this chilling story and an ancient optimism among the Egyptians is worth noting. Initially life after death was limited to the king in ancient Egypt. Over the centuries, a kind of democratization of the afterlife took hold and the chance for renewed life was open to us regular sorts as well. In a snapshot of how religions work, this transformation holds the keys for further religious developments. The benefits trickle down from the elite to the peasant. Those who awake in the morgue may count themselves lucky since Osiris demands their presence only at a later date.
Modern ideas of resurrection are great motivators for religious belief. The fact that Paleolithic burials sometimes include grave goods demonstrates that some kind of afterlife hope predates civilization itself. It is one of the formative elements of religion. In a world where death may not be the worst possible fate, however, such an afterlife may eventually lose its drawing power. For Egyptian peasants, the afterlife was pretty much a continuation of peasant life. I suspect that those who wake up in a morgue have a new perspective on life after death that most of us, thankfully, never have to face.