The other day I was reading about monasticism (as one does), and something curious occurred. The article, which was describing a famous monastery, mentioned that monks lived in the convent. Now, lest you think anything about religion is simple, I must clarify that in English it is common usage to refer to “monasteries”as places where monks (male) live. Again, in English usage “convents”are for nuns (female). The words, however, have a more interesting history than that. Not exactly interchangeable (can you imagine the confusion?), they do originally refer to different kinds of institution.
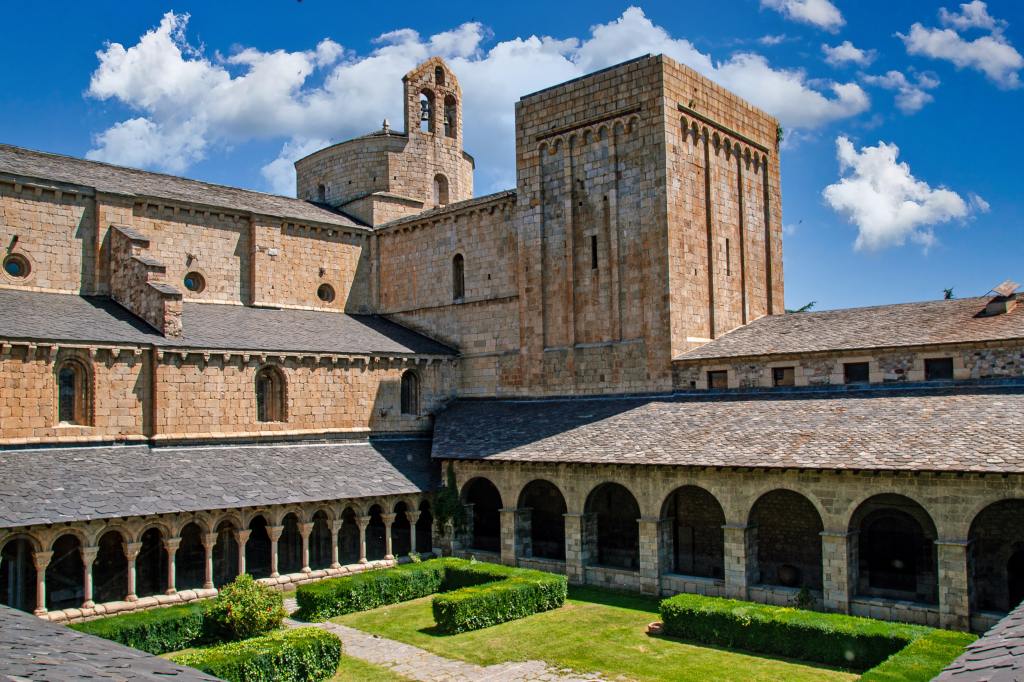

Often monasticism is traced back to Anthony of Egypt. Anthony famously kept himself away from other people to devote his life to God. This, of course, led other people to seek him out, wanting what he’d found. Eventually, the narrative goes, the idea occurred that lots of guys could live together in common, but shut away from the rest of the world. Thus monasteries were born. The story’s actually more complicated and I can’t give you the full picture here. We do know that even in Judaism, before Christianity came along, there were separatist sects. One of them, known for convenience as “the Essenes,” set up a commune not far from where the Dead Sea Scrolls were discovered. They lived lives of purity and prayer and women were strictly forbidden. They seem even to have had a monastic rule. They lived on the edge of the desert and perhaps were responsible for the famous scrolls. Monasticism thus had early roots.
The European Middle Ages were the high-water mark for monasticism. Like our own day, people were dealing with plagues and strong-arm kings and lack of adequate infrastructure. Many powerful monasteries had been founded, and they could be for monks or nuns, generally not in mixed company. There were also solitary monks (it was more difficult for women to wander about alone), called mendicants. Such people needed places to stay now and again, and that was what was called a convent. A monastery could be for either sex, and the word “nunnery”eventually helped to make this clear. The English use of the words, while convenient, can lead to confusion because established monasteries could have convents as part of their design. I suppose not many people are really interested in monasticism these days. Looking at what’s happening in the world, however, I wonder if we might not be on the cusp of a modern replacement for them. It would be something curious indeed.